01x06_ctrl_alt_disrupt.bat
In this episode we look at one of Defender XDRs most exiting features at the moment: Attack Disruption! Why it is so exiting and how you can start using it today?
Defender XDR Attack Disruption
Attack Disruption automatically identifies compromised assets and it will be able to stop attackers in their tracks in real-time. So, while the attack is happening!
It’s not new. It’s around since somewhere in 2023. But new features are added constantly and I think it’s one of the most exciting features of Defender XDR!
Attack Disruption is not primarily about detection. Most security products today will work like this: “we saw certain events, here’s the evidence, please investigate it and respond”. Microsoft wants to move away for this and provide actual protection and stop the attackers when they’re active.
By combining multiple Security products, bring signals together to dynamical and automatically detect and response to a threat. According to Microsoft it does this “in real-time” (“at machine speed” ;-) ) and “with high confidence” to contain and prevent (further) damage.
Works in several different stages
-
Detection
Correlated sign as from multiple sources are combined into a single high-confidence incident
-
Correlation
Classify attack scenario and identify assets controlled by the attacker Couple of scenario’s which are supported by Attack Disruption are: Human Operator Ransomware, Business email compromise, Adversary in the middle and Password Spray attacks among other.
-
Intent Recognition
Understand the intent of the attacker to accurately predict their next move & identity attack scenario. This is not pre-determined but dynamically build based on your organizations Attack Paths.
-
Attack Disruption
As the attack evolves it automatically identifies compromised assets (users, devices, mailboxes, apps, …) to determine a “blast radius” 🧨 within your network. It will then be able to suspends compromised assets in real-time.
-
AI-powered automation
(Because we need some AI in our product of course 😎) Leaves the SOC in full control of investigation and remediating but limits the impact of an attack by stopping lateral movement.Respond actions currently supported:
- Device contain
- User contain
-
Disable user
But also first third-party support with SAP with Microsoft Sentinel. For example contain compromised assets by locking suspicious SAP users in case of a financial process manipulation attack.
They’re not only using signals from multiple different products (Endpoint, Office, Cloud Apps….) but also using these product to respond/contain the attack.

For example MDE is used to contain the device and prevent lateral movement, while EntraID is used to contain the user AND MDI is used to contains the on-prem users. Also to prevent having to rely on a sync. The fast to disrupt the attack the better
A real-world example of Business e-mail compromise (BEC) and adversary in the middle attack (AitM)
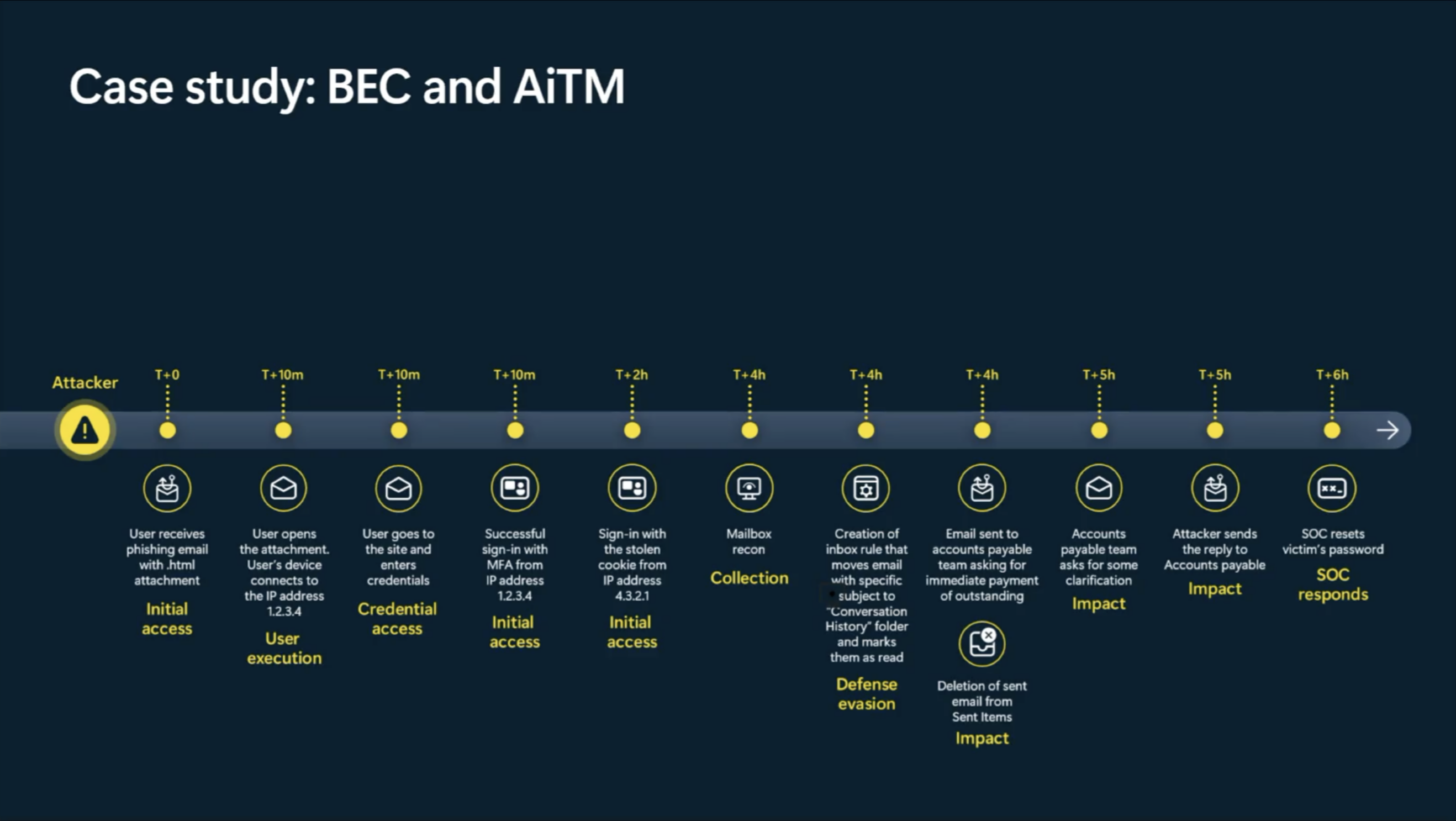
Not only was attack disruption able to disable a compromised account. It was able to detect the AitM attack as well and invalidate the token of that compromised account.

Customer Grading
How customers respond (and other kinds of signals and behavior) determines the quality of the signal-to-noise ratio. According to Microsoft: only < 1% of false positives (99%+ true positive rate)
Due to the impactful native of the respond actions, attack disruption is designed to rely on high-fidelity signals only.
Microsoft learns from customer behavior surrounding a “attack disruption” type of incident.
You can look in your security portal and search for incidents with an “attack disruption” tag to find earlier incidents where Microsoft did perform some automated response actions.
Microsoft also learns from attack disruption incidents across orgs and harvest telemetry data to intervene ever quick at other customers.
According to Microsoft they’re disrupting 40.000 incidents a month.
How to use
Attack Disruption is enabled by default. But there are certain configurations you should look into for optimal usage.
Defender for Endpoint
- Attack disruption relies heavily on Defender for Endpoint’s discovery and contain capabilities. Go to Settings –> Device discovery and make sure that Discovery mode is set to “Standard” (not basic) for “all devices”.
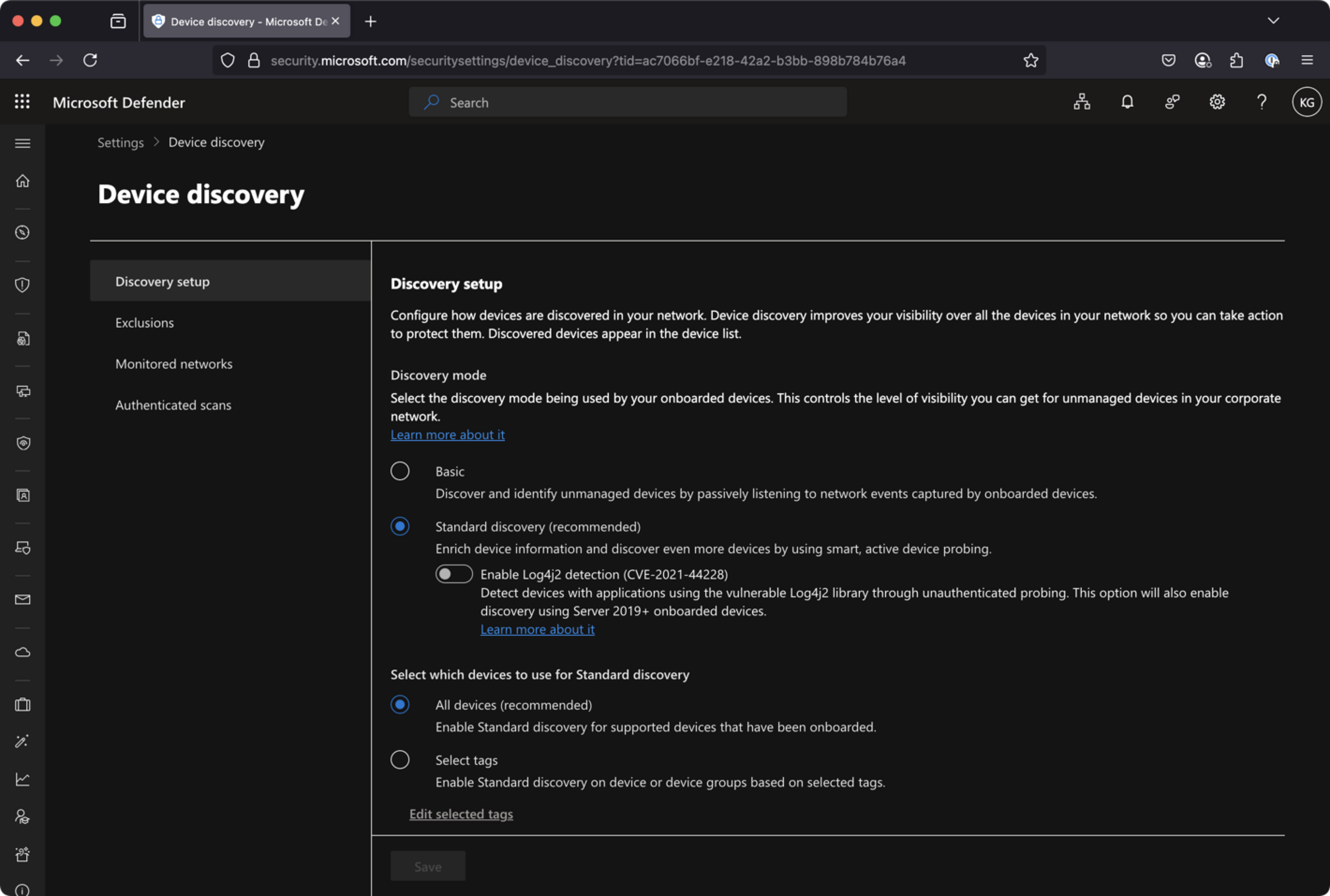
You can always check if there are any discovered devices in your environment:
DeviceInfo
| summarize arg_max(Timestamp, *) by DeviceId // Get latest known good per device Id
| where isempty(MergedToDeviceId) // Remove invalidated/merged devices
| where OnboardingStatus != "Onboarded"
-
Make sure your automation is set to
Full Remediation. Go into Settings –> Endpoint –> Device Groups –> Remediation level. -
Endpoint need to run Sense agent
v10.8470or newer. Check theDeviceTvmSoftwareInventorytable to verify and find outdated clients
DeviceTvmSoftwareInventory
| where SoftwareVendor has "microsoft" and SoftwareName has "defender_for_endpoint"
| extend MajorVersion = toint(split(SoftwareVersion, '.')[0])
| extend MinorVersion = toint(split(SoftwareVersion, '.')[1])
| where MajorVersion == 10
| where MinorVersion < 8470
- Perhaps needless to say, but you need to make sure that all of your devices run Defender for Endpoint. Regularly check for non-onboarded discovered in your environment. (Devices –> Assets)
DeviceInfo
| where OnboardingStatus != "Onboarded"
| summarize lastSeen = arg_max(Timestamp, *) by DeviceId
| where isempty(MergedToDeviceId)
| limit 100
| invoke SeenBy()
| project lastSeen, DeviceId, DeviceName, DeviceType, SeenBy
Defender for Identity
Within Defender for Identity you need to check your “Action Accounts”. (Settings –> Identities –> Manage action accounts)
Here you have two options:
- Automatically use sensor’s
local systemaccount - Manually configure and use a Group Managed Service Account (gMSA)
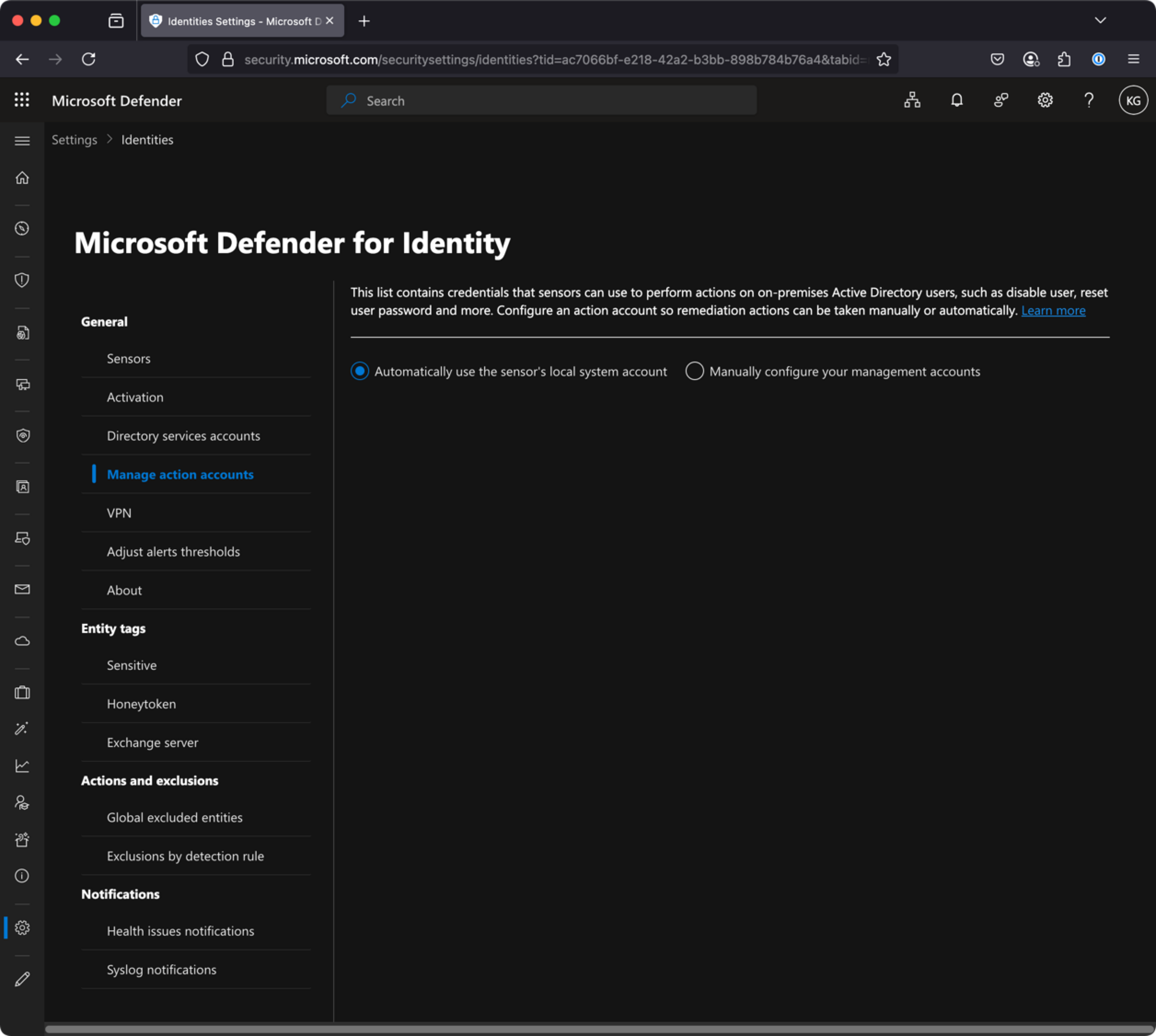
If you have chosen the latter, make sure that account still exists!
Also make sure all your sensors are healthy. Because MDI relies heavily on proper setup of auditing policies.
Defender for Cloud Apps
- Microsoft Defender for Cloud Apps must be connected to Microsoft Office 365 through the connector. Check the instructions here.
- App Governance must be turned on. Check the app governance documentation on how to turn it on.
Defender for Office 365
- Mailboxes are required to be hosted in Exchange Online
- The following mailbox events need to be audited by minimum:
- MailItemsAccessed
- UpdateInboxRules
- MoveToDeletedItems
- SoftDelete
- HardDelete
- Safelinks policy needs to be present
SAP
- To use attack disruption for SAP, deploy a data connector agent
Notifications
I think it’s good practice to enable some form of notifications for certain actions (i.e. disable user, contain device). For example a user gets disabled, and within a short while somebody else tries to resolve an issue by enabling this user again.
It’s useful to notify stakeholders about the fact that someone (including Microsoft’s attack disruption) took this action.
Exclusions
You can also exclude certain device groups/entities from Attack Disruption. It’s not recommended! But sometimes necessary.
Settings –> Defender XDR –> Automated Response –> Identities/Devices
This incident will still trigger but with a “failed” action status.
Read more
- Microsoft’s documentation on Attack Disruption
- Microsoft Defender XDR Attack Disruption Prerequisites
- Shoutout to former-colleague Jeffrey Appel who wrote a lot about Defender XDR in the past.
🛠️ Community Project
Microsoft 365 Security Incident Investigation Tool (for Exchange Online)
Microsoft MVP Mezba Uddin has created a PowerShell script to help administrators investigate and respond to potential security incidents in Exchange Online. The script can perform six specific investigation actions in Exchange Online. Each action targets a common post-incident scenario using either audit log searches or Graph API queries, depending on what’s most effective for the individual scenario:
- Malicious Inbox Rules Detection
- Unusual Email Volume Detection
- Mailbox Permission Changes Monitoring
- Critical Email Deletion Detection
- Mailbox Export Monitoring
Check it out on Github